Last week’s Writing-Tip Wednesday post began a two part series on dialogue with some advice on the writing of the actual “spoken” words we put in the mouths of our characters. Today, I follow that up with a discussion of dialogue attribution. This is a very long post, which includes lengthy excerpts from my work that should serve to illustrate the points I’m trying to make. I hope you’ll stick with it to the end.
Identifying the speaker in written conversations is one of the most difficult things we do as writers. It seems so simple, right? All we’re trying to do is tell the reader who said what. And yet it is so easy to do this poorly. Part of the problem is that, as with the dialogue itself, everything we try to do in this regard must strike a balance. Too heavy a hand, and our dialogue tags sound clunky. Too light a hand, and our readers lose track of who is speaking. Take too limited an approach and the tags start to sound boring and repetitive.
I am a huge fan of the Harry Potter books. Our daughters loved them and Nancy and I wound up enjoying them immensely as well. We have read the entire series multiple times and listened to them on audiobook during many a family roadtrip. I think J.K. Rowling does many things very, very well as both a writer and a storyteller. But in listening to her books on audio and I came to realize that her dialogue attribution is terrible. Why? Because it is unimaginative and repetitious. She resorts to “said Harry,” “said Hermione,” “said Ron,” with almost every line.
So how do we avoid that?
Let’s start by defining some terms. Dialogue tags are words we use as direct attribution – “he said,” “she asked.” Said-bookisms are dialogue tags run amok. They are direct attribution but with more descriptive verbs – “he hissed,” “she growled,” “he averred,” “she opined,” “he remarked,” “she exclaimed,” etc. At times, I will speak of using action, emotion, or mannerism to identify the speaker. By this I mean starting a paragraph with, say, “Kannice brushed a strand of hair from her brow,” before having her speak. And finally unattributed dialogue is simply a line of dialogue that has no other sort of identifier except the spoken words themselves.
In these definitions, we see three broad approaches to identifying the speakers in our written conversations. We can use dialogue tags. We can use action and mannerisms. We can let the spoken words stand alone and unattributed.
When it comes to using these various approaches, there are several schools of thought. I have writer friends who swear that we should NEVER use direct tags of any sort. No “said”s, no “asked”s, and certainly no “hissed”s or “opined”s. And I should add here that said-bookisms are generally frowned upon in all segments of the market these days. They are considered “telling” rather than “showing,” and thus seen as evidence of bad writing. The things said-bookisms might tell us are better conveyed with context, with the spoken dialogue itself, and with other descriptive tools. Some people are VERY strict in their rejection of said-bookisms and the like. I’m not. In addition to “said” and “asked” I will use a few words that convey volume (“whispered,” “called,” “muttered,” “shouted”) and sometimes one or two that supply context and rhythm (“went on” or “added”). I am VERY sparing in my use of these words. Mostly, when I use tags, it’s “said” and “asked.”
There are also benefits and drawbacks to each of these approaches. Dialogue tags offer the most clarity, but, as with the Harry Potter books, they can be boring, even pedestrian. Unattributed dialogue flows most smoothly and can be very dramatic and fast-paced when used well. But after a few lines, readers have to start counting back to figure out who is saying what. (And as mentioned last week, we SHOULD NOT deal with this by having characters call one another by name with any frequency.) Finally, using mannerism, emotion, and action can be an elegant way of identifying the speaker, one that also adds details and emotional cues that tell the reader a lot. But overuse of them makes our characters seem unnaturally twitchy; mannerisms can quickly turn into tics, which we don’t want.
With all of that in mind, it probably won’t surprise any of you to learn that I suggest using a mix of the three techniques of attribution. Some lines, I feel, should be attributed directly. Some should stand on their own without attribution. And in some cases the speaker should be identified in some other way – facial expression, gesture, action, etc. By way of example, here is a passage from Time’s Demon, the second Islevale Cycle book. This is the scene in which the Tirribin, Droë first encounters the Arrokad, Qiyed:
Water ran down his body as he stepped from the surf and halted in front of her.
“There is a price to be paid for summoning my kind, even for one such as you, cousin.”
“I know. What price?”
“We shall decide, you and I. Why have you summoned me?”
She opened her mouth to answer, but no words came. Instead, to her shame, she burst into tears. For some time, too long, she could not speak for her sobbing. The Arrokad regarded her, unmoving and apparently unmoved.
When at last she found her voice, she apologized.
“What is your name, cousin?”
“I am Droënalka. Most call me Droë.” She would have expected a human or another Tirribin to reciprocate, but such conventions did not apply to the Most Ancient Ones. Either he would tell her his name or wouldn’t. His to choose.
“Do you seek a boon, Droë of the Tirribin? Is this why you summoned me?”
She hesitated before nodding.
“I see. That, too, carries a cost.”
“I know that,” she said, wearying of being spoken to as if she knew nothing. “I’m Tirribin. I understand the commerce of summons and boon.”
A canny smile revealed gleaming sharp teeth. “Better. That is the spirit I expect when treating with Tirribin. I had begun to think you simple.”
“That’s rude.” But his teasing made her feel better, more like herself.
“Yes, I suppose it is. I am Qiyed. You showed great restraint in not asking. I know how much your kind care about etiquette.”
Her cheeks warmed.
“Tell me more of this boon you seek.”
“I– I don’t know how.”
“That is intriguing, but I do not wish to remain on this strand for long.” Lightning flashed, and thunder followed, sooner than she had expected. “A storm comes, and I long to swim with it.” Another sly grin. “Have you ever done this?”
“No.”
“Would you care to?”
She reflected with distaste on her swim from the ship. “I don’t think so, no.”
“Very well. Quickly then.”
Where to begin?
“There is a Walker. I’m told I knew him when he trained in the palace at Trevynisle.”
“You have come from the northern isles?” he asked, surprise in the question.
“Yes.”
“And what does that mean: ‘I’m told I knew him’?”
“He traveled back in time, and created this misfuture we’re in now. The humans have fought over Hayncalde in Daerjen. One supremacy has given way to another.”
“I knew nothing of this.”
She canted her head. “Payment for my summons?”
He bared his teeth again. “Clever, cousin.” He considered this. “Done. That part of your debt to me is paid in full. Go on.”
As you can see here, I use a lot of dialogue to establish their relationship, and I blend direct attribution with emotion and gesture, while also leaving a few lines to stand for themselves, without any tag or other cue as to who is speaking. And yet, we never lose track of the conversation. Clearly, this becomes more difficult when we introduce a third character (and a fourth or fifth or sixth). The more people in the scene, the more often we need to identify the speaker.
Here is a second scene, this one among three characters, one a woman who has Walked through time and met herself in the past, at the expense of her sanity, and the other two the Tirribin siblings, Maeli and Teelo.
At a stirring of the wind, she caught the fetor of decay and she glanced around again. The smell dissipated as swiftly as it had come.
“I suppose I should be on my way,” she said, after the silence had lengthened uncomfortably.
“I can’t tell what it is,” the girl said in a voice both childlike and knowing. “Can you?”
The boy shook his head. “Not at all. At least not beyond the obvious.”
“Its years are all–”
“Who are you?” she asked. “Why are you talking about me that way?”
“We’re having a conversation,” the girl told her, as haughty as a court noble. “And you’re interrupting. That’s rude.”
She had to smile. “Isn’t it just as rude to talk about someone in their presence, as if they aren’t there?”
The two shared a look, worry in their ghostly eyes.
“Yes, it is,” the girl said, chastened. “Please forgive us.”
“Children shouldn’t be out alone in the streets. You should go home”
The girl hid her mouth with a thin hand, her laughter as clear and musical as the splash of a brook. “We’re not children. You should know that.”
She stared at one and then the other, puzzled now. If not children… Were they creations of her mind, symptoms of her madness? She thought she understood the depths of this Walking induced insanity. What if she was wrong, and it continued to worsen? What if these two marked the beginning of a slide into hallucination?
“You’ve confused it,” the boy said. “Maybe it doesn’t know as much as we hoped.”
She scowled. “Stop referring to me as ‘it.’”
“What else would we call you?”
“‘She,’ of course.”
He shook his head. “You’re not a she, are you? You’re not really anything at all.”
“I don’t–”
“We tasted your years when you were still on the sand,” the girl said. “That’s why we called for you. We sensed the confusion in you, and we wanted to know exactly what you are. But you don’t know yourself.”
We tasted…
“You’re Tirribin,” she said, drawing on a memory from so long ago, it could have been a different life. She took a step back from them. “That’s why…” She stopped herself from mentioning the smell. “Why you could taste my years from so great a distance.”
The girl glowered, appearing to know what Lenna intended to say.
“That’s right,” the boy said. “We’re Tirribin.” To his sister, he said, “Maybe she knows more than we thought.”
Suspicion lingered in the girl’s glare. “I’m not so sure. You don’t need to fear us,” she said, a rasp underlying the words. “Your years are muddied. We wouldn’t feed on you any more than a human would drink sea water. It would do more harm than good.”
“Why? What’s wrong with them?” She feared their answer.
“Don’t you know?”
Of course she did. Tirribin didn’t prey on Walkers because their years were less pure. She remembered a time demon explaining this to her when she was a child in Windhome. Before a boy died and another was sent away. Now she was here, fourteen years out of her time, twelve days out of another, half-mad from having met herself. Whose years could be less pure than hers?
“Yes,” she said. “I know. But that doesn’t make me less than human, and it doesn’t excuse you calling me ‘it.’”
“You’re a creature outside of time,” the girl said with relish. “There are too many of you, and your years are beyond repair.” She made a small gesture, indicating the lane and the houses. “You bear little resemblance to the humans I sense around me.”
“Maeli…”
The girl rounded on the other demon. “Don’t tell me I’m being rude. She was going to say something about the way we smell. Humans do that a lot, and I grow tired of it.”
“What should I do?” Lenna asked, drawing their attention once more.
The girl laughed again, the sound uglier than before. “Do?”
“Don’t you intend to help me? Isn’t that why you called to me?”
“We’re Tirribin. We’re predators, and while your years would be disgusting to us, that doesn’t make you more than prey.”
The boy frowned but held his tongue.
“And even if that weren’t so, there would be no helping you. You are what you are, and can’t be changed or redeemed. You didn’t exist before today. I can tell. Yet you have all these years. Confused, corrupted, but years nevertheless. We didn’t call you here to help. We called to see you. We sensed you, and we wanted to see what sort of being could have such years.” The girl raked her up and down with her gaze. “Honestly, I thought you would be more interesting than you are. You seem no different from other humans.”
“Then maybe you’re wrong about me.”
The Tirribin shook her head. “I’m not.”
The process is trickier here, because of the number of characters, but still I have done my best to use all the techniques at my disposal in a way that keeps the narrative flowing and keeps the speakers clear in the minds of readers.
A few other points and then I will end what is already a very long post: First, punctuating and formatting dialogue is a little complicated. Pay attention to how I have done so in these examples and keep in mind that whenever you change who is speaking or reacting, you need to start a new paragraph. Also remember that things like laughter or sighs are NOT dialogue tags. They are actions/mannerisms. You can’t say, “‘That’s funny,’ he laughed.” But you can say, “‘That’s funny.’ He laughed.” See the difference?
Finally, remember this: Writing dialogue is fun, just as reading it is fun. It’s also hard and takes some time to master. I’ve been doing this for 25 years. It took me a while to get to where I feel comfortable using a variety of techniques to attribute my lines of dialogue. You’ll get there as well. For now, your priorities should be remaining true to your characters’ voices and being totally clear about who is speaking. I find that it’s easier to remove tags and other identifiers than it is to put more in, so I always err on the side of clarity, knowing that I can clean things up in revisions.
Best of luck with this, and keep writing!









 As you know at this point, we are in the midst of release week for
As you know at this point, we are in the midst of release week for  The truth is, I have felt that way about all three volumes of this trilogy. The Islevale books were incredibly difficult to write. I knew going in that writing time travel would be really hard — as one friend told me, “It’ll make your brain explode.” So much can go wrong. We have to examine every plot point from every possible angle to make certain it holds up to logic, and to the simple reality that time travel gives us endless opportunities for do-overs. Put another way, every event in a time travel story is negotiable. Each one can be altered or reversed by the very plot devices on which our stories depend.
The truth is, I have felt that way about all three volumes of this trilogy. The Islevale books were incredibly difficult to write. I knew going in that writing time travel would be really hard — as one friend told me, “It’ll make your brain explode.” So much can go wrong. We have to examine every plot point from every possible angle to make certain it holds up to logic, and to the simple reality that time travel gives us endless opportunities for do-overs. Put another way, every event in a time travel story is negotiable. Each one can be altered or reversed by the very plot devices on which our stories depend. I hoped that
I hoped that  I frequently tell beginning writers that they need to self-define success, something which is really hard to do in this business. All too often we writers are forced by the nature of publishing to seek exterior affirmation for our work — reviews, sales, awards if we’re fortunate enough to win them. These are the things the industry values and so, naturally, they are the things we care about as well. The problem with this is, the industry is cruel and capricious. We all know of good, even great, books that go unnoticed and unacknowledged. We all have seen mediocrity rewarded with terrific sales and undeserved attention. And we know that this is true in the world beyond publishing as well. Life is not always fair.
I frequently tell beginning writers that they need to self-define success, something which is really hard to do in this business. All too often we writers are forced by the nature of publishing to seek exterior affirmation for our work — reviews, sales, awards if we’re fortunate enough to win them. These are the things the industry values and so, naturally, they are the things we care about as well. The problem with this is, the industry is cruel and capricious. We all know of good, even great, books that go unnoticed and unacknowledged. We all have seen mediocrity rewarded with terrific sales and undeserved attention. And we know that this is true in the world beyond publishing as well. Life is not always fair. I’ve just finished working on a set of three novellas set in the
I’ve just finished working on a set of three novellas set in the  …And allow me take a moment to urge you get a copy of Time’s Assassin. (
…And allow me take a moment to urge you get a copy of Time’s Assassin. ( Let’s start with what I mean when I speak of multiple point of view characters. This is NOT an invitation to jump willy-nilly from character to character, sharing their thoughts, emotions, and sensations. That is called head-hopping, and it is considered poor writing. Rather, writing with multiple point of view characters means telling the story with several different narrators, each given her or his own chapters or chapter-sections in which to “tell” their part of the story. When we are in a given character’s point of view, we are privy only to her thoughts and emotions. In the next chapter, we might be privy to the thoughts of someone else in the story. This is an approach used to great effect by George R.R. Martin in his Song of Ice and Fire series. Martin goes so far as to use his chapter headings to tell us who the point of view character is for that section of the story. Guy Gavriel Kay uses multiple point of view quite a bit – in Tigana, in his Fionavar Tapestry, in many of his more recent sweeping historical fantasies. I have used it in my epic fantasy series – The LonTobyn Chronicle, Winds of the Forelands, Blood of the Southlands, The Islevale Cycle.
Let’s start with what I mean when I speak of multiple point of view characters. This is NOT an invitation to jump willy-nilly from character to character, sharing their thoughts, emotions, and sensations. That is called head-hopping, and it is considered poor writing. Rather, writing with multiple point of view characters means telling the story with several different narrators, each given her or his own chapters or chapter-sections in which to “tell” their part of the story. When we are in a given character’s point of view, we are privy only to her thoughts and emotions. In the next chapter, we might be privy to the thoughts of someone else in the story. This is an approach used to great effect by George R.R. Martin in his Song of Ice and Fire series. Martin goes so far as to use his chapter headings to tell us who the point of view character is for that section of the story. Guy Gavriel Kay uses multiple point of view quite a bit – in Tigana, in his Fionavar Tapestry, in many of his more recent sweeping historical fantasies. I have used it in my epic fantasy series – The LonTobyn Chronicle, Winds of the Forelands, Blood of the Southlands, The Islevale Cycle. This is in contrast with single character point of view, in which we have only one point of view character for the entire story (and that point of view can be either first or third person). Think of Haith’s Yane Jellowrock series, or my Thieftaker or Justis Fearsson series, or Jim Butcher’s Harry Dresden books, or Suzanne Collins Hunger Games series, or even (for the most part) J.K. Rowling’s Harry Potter books.
This is in contrast with single character point of view, in which we have only one point of view character for the entire story (and that point of view can be either first or third person). Think of Haith’s Yane Jellowrock series, or my Thieftaker or Justis Fearsson series, or Jim Butcher’s Harry Dresden books, or Suzanne Collins Hunger Games series, or even (for the most part) J.K. Rowling’s Harry Potter books. For single character point of view we have essentially two kinds of books: urban fantasies that have a mystery element, and YA novels that concentrate as much on the lead character’s emotional development as on external factors. Single character POV tends to be intimate. Readers form a powerful attachment to the narrators of these books. And, of even greater importance, readers learn things about the narrative at the same time the characters do. Even in books that begin with our narrator looking back on past events, we are soon taken back in time so that this older narrative has a sense of immediacy. This is why single character POV works so well in mysteries. The reader gets information as the “detective” does. Discovery happens in real time, as it were.
For single character point of view we have essentially two kinds of books: urban fantasies that have a mystery element, and YA novels that concentrate as much on the lead character’s emotional development as on external factors. Single character POV tends to be intimate. Readers form a powerful attachment to the narrators of these books. And, of even greater importance, readers learn things about the narrative at the same time the characters do. Even in books that begin with our narrator looking back on past events, we are soon taken back in time so that this older narrative has a sense of immediacy. This is why single character POV works so well in mysteries. The reader gets information as the “detective” does. Discovery happens in real time, as it were.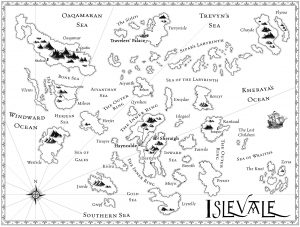 And then I just let my imagination run wild. At first I let my hand wander over the page, creating the broad outlines of my world. Sometimes I have to start over a couple of times before I come up with a design I like. But generally, I find that the less I impose pre-conceived notions on my world, the more successful my initial efforts. I draw land masses, taking care to make my shorelines realistically intricate. (Take a look at a map of the real world. Even seemingly “smooth” coastlines are actually filled with inlets, coves, islands, etc.) I put in rivers and lakes. I locate my mountain ranges, deserts, wetlands, etc.
And then I just let my imagination run wild. At first I let my hand wander over the page, creating the broad outlines of my world. Sometimes I have to start over a couple of times before I come up with a design I like. But generally, I find that the less I impose pre-conceived notions on my world, the more successful my initial efforts. I draw land masses, taking care to make my shorelines realistically intricate. (Take a look at a map of the real world. Even seemingly “smooth” coastlines are actually filled with inlets, coves, islands, etc.) I put in rivers and lakes. I locate my mountain ranges, deserts, wetlands, etc.